About Rubus berries
According to Wikipedia, Rubus is a large and diverse superspecies of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, subfamily Rosoideae, with 250–700 species.
Raspberries, blackberries, and dewberries are common, widely distributed members of the genus. Most of these plants have woody stems with prickles like roses; spines, bristles, and gland-tipped hairs are also common in the genus.
The Rubus fruit, sometimes also known as a bramble fruit, is an aggregate of drupelets. The term “cane fruit” (or “cane-fruit”), or “cane berry” (or “caneberry”), applies to any Rubus species or hybrid which is commonly grown with supports such as wires or canes, including raspberries, blackberries, and hybrids such as loganberry, boysenberry, marionberry and tayberry. The stems of such plants are also referred to as canes.
The Mulberry – so named because of its similar looking fruit to Rubus – is actually from a completely different botanical family and form a tree as opposed to a cane or trailing bramble.
RASPBERRIES
Raspberries are traditionally grown in climates with cold winters, which provide the plant with required chill, and crop most abundantly from early November until May.
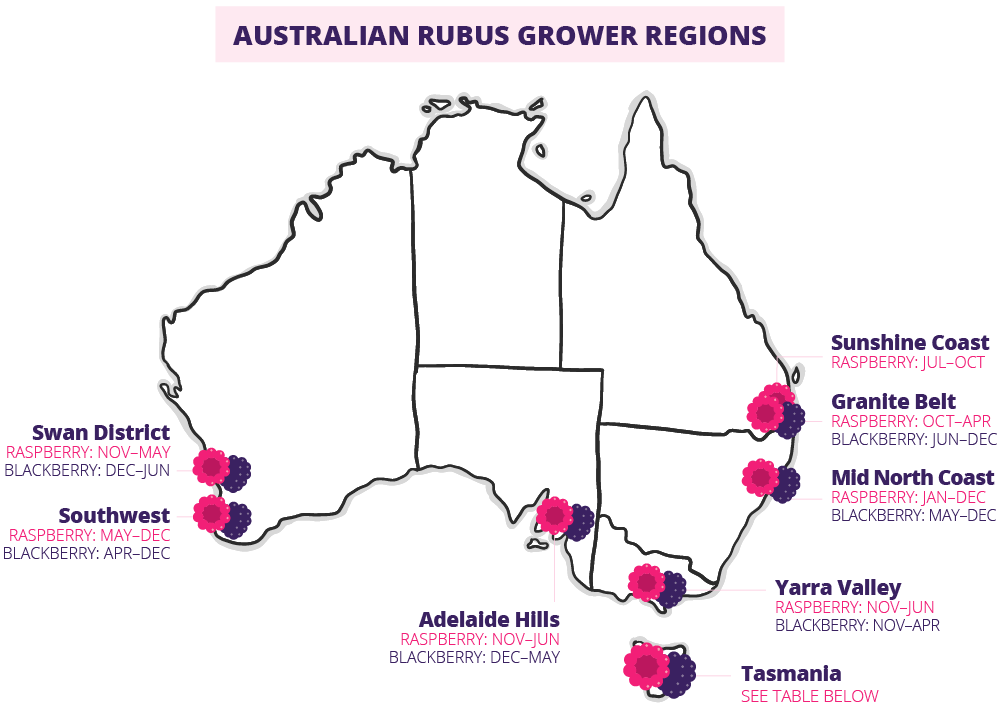
More recently, warmer climate plantings (producing in winter and spring) have allowed fresh Australian raspberries to become available in supermarkets and green grocer stores almost all year round. The raspberries that are available in the winter/spring months are grown in northern NSW, southern QLD, and near Perth.
There are a range of varieties of raspberries; some are lighter in colour while others are a deep red when ripe. All raspberries have similar nutritional profiles.
BLACKBERRIES
Blackberries are mostly grown in southern regions of Australia and are available from early November until April.
There are several varieties that fruit sequentially, to provide a range of berries from dark-coloured round fruit, to elongated berries available across the period. Each variety of blackberry has its own unique flavour, varying in aroma, acidity and strength of flavour.
About Rubus in Australia
There are approximately 120 growers producing raspberry and blackberry crops across all states except the Northern Territory, with negligible amounts in Western Australia. The majority of berries are produced in the southern states of Australia, particularly in the Dandenong Ranges and Yarra Valley regions of Victoria, Corindi in New South Wales and the Northern Midland region in Tasmania. Other production areas in Queensland, South Australia and Western Australia extend seasons for year-round supply.
Australian raspberry and blackberry (species of the rubus genus) production is dominated by raspberries, which accounted for 86 per cent of fresh production for the year ending June, 2018. Blackberries accounted for 13.5 per cent of fresh production, with other rubus varieties such as silvanberries, boysenberries and loganberries equating to less than one per cent of production.
Industry production growth
The main growing season is November to May (summer and autumn), with the greatest volume produced from December to April. However, fresh berries are now available year round, with crops being increasingly grown undercover and more production being established across multiple states. The capacity to provide year-round supply has helped the industry to develop sustained retail sales growth through national supermarket chains.
Production volumes have increased rapidly, rising from 2,167 tonnes ($70.6 million) in 2013 to 6,189 tonnes ($157.3 million) in 2018. This equates to an approximate 300 per cent increase in the volume of berry production over the last five years and has supported strong year-on-year sales growth and per capita consumption.
The rapid increase in production has seen a significant shift in the structure of the industry, from smaller businesses based mostly in the Yarra Valley in Victoria, towards larger corporate plantings in diverse locations around Australia.
Source: Hort Stats Handbook 2017/18